The Complete Guide to Cannabis Terpenes: Aromas, Effects & The Big 6
Master the 6 major cannabis terpenes: myrcene, limonene, pinene, linalool, caryophyllene & terpinolene. Learn how they shape your high.
Professor High
Your friendly cannabis educator, bringing science-backed knowledge to the community.
If you’ve ever wondered why two strains with identical THC percentages produce completely different experiences, terpenes are your answer. These aromatic compounds do far more than make your cannabis smell like pine, citrus, or lavender - they fundamentally shape how you feel when you consume it.
Cannabis contains over 200 identified terpenes, but you don’t need to memorize all of them. Understanding just six major terpenes will transform how you select strains and predict your experiences. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the science, the aromas, and the effects of each - backed by the latest 2024-2025 research.
Let’s dive into the fascinating world of terpenes.
What Are Terpenes?
Terpenes are aromatic compounds found in virtually every plant on Earth - not just cannabis. They’re responsible for the scent of pine forests, the zing of citrus peels, the calming aroma of lavender fields, and the spicy kick of black pepper. In nature, they serve as defense mechanisms against predators and attractants for pollinators.

Where Terpenes Come From
In cannabis, terpenes are produced in the same structures that create cannabinoids: the trichomes. These tiny, mushroom-shaped glands that give premium flower its frosty appearance are essentially chemical factories, synthesizing both the cannabinoids (THC, CBD, CBG) and the terpenes that define each strain’s unique profile.
Here’s what makes this interesting: terpenes and cannabinoids share the same biosynthetic pathway. They’re created from the same precursor molecules, which is why high-quality cannabis with rich cannabinoid content typically also has robust terpene profiles. A 2025 German study found a moderate correlation (r = 0.41) between THC content and total terpene levels.
More Than Just Smell
For decades, the cannabis industry treated terpenes as mere aromatics - nice for marketing, but not particularly important for effects. That assumption has been thoroughly debunked by modern research.
Terpenes contribute to cannabis effects through multiple mechanisms:
| Mechanism | How It Works | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Direct receptor binding | Some terpenes activate cannabinoid receptors | Caryophyllene binds to CB2 |
| Receptor modulation | Terpenes change how cannabinoids interact with receptors | Limonene modulates CB1/CB2 |
| Membrane permeability | Terpenes help cannabinoids cross the blood-brain barrier | Myrcene increases permeability |
| Alternative receptors | Terpenes activate non-cannabinoid receptors | Linalool modulates NMDA receptors |
This multi-pathway activity is why the same THC percentage can produce wildly different experiences depending on the terpene profile. It’s also the foundation of the entourage effect - the phenomenon where cannabis compounds work synergistically to produce effects none could achieve alone.
The 200+ Terpene Reality
While cannabis produces over 200 different terpenes, most strains are dominated by a handful of major players. A 2025 analysis of 140 medicinal cannabis strains found that just 9 terpenes explain 86% of the chemical variation between strains.
For practical purposes, you can understand most cannabis experiences by learning the “Big 6” terpenes we’ll cover below. Master these, and you’ll have a working knowledge that covers the vast majority of strains you’ll encounter.
The Big 6: Your Essential Terpene Guide
Let’s break down the six most important terpenes in cannabis - the ones that shape the majority of cannabis experiences and the ones you’ll see most often on lab results.
1. Myrcene: The Couch-Lock Terpene
Myrcene is the most common terpene in cannabis, often making up 20% or more of a strain’s total terpene profile. If you’ve ever experienced “couch-lock” - that heavy, sedating body high that makes standing up feel optional - you’ve felt myrcene at work.
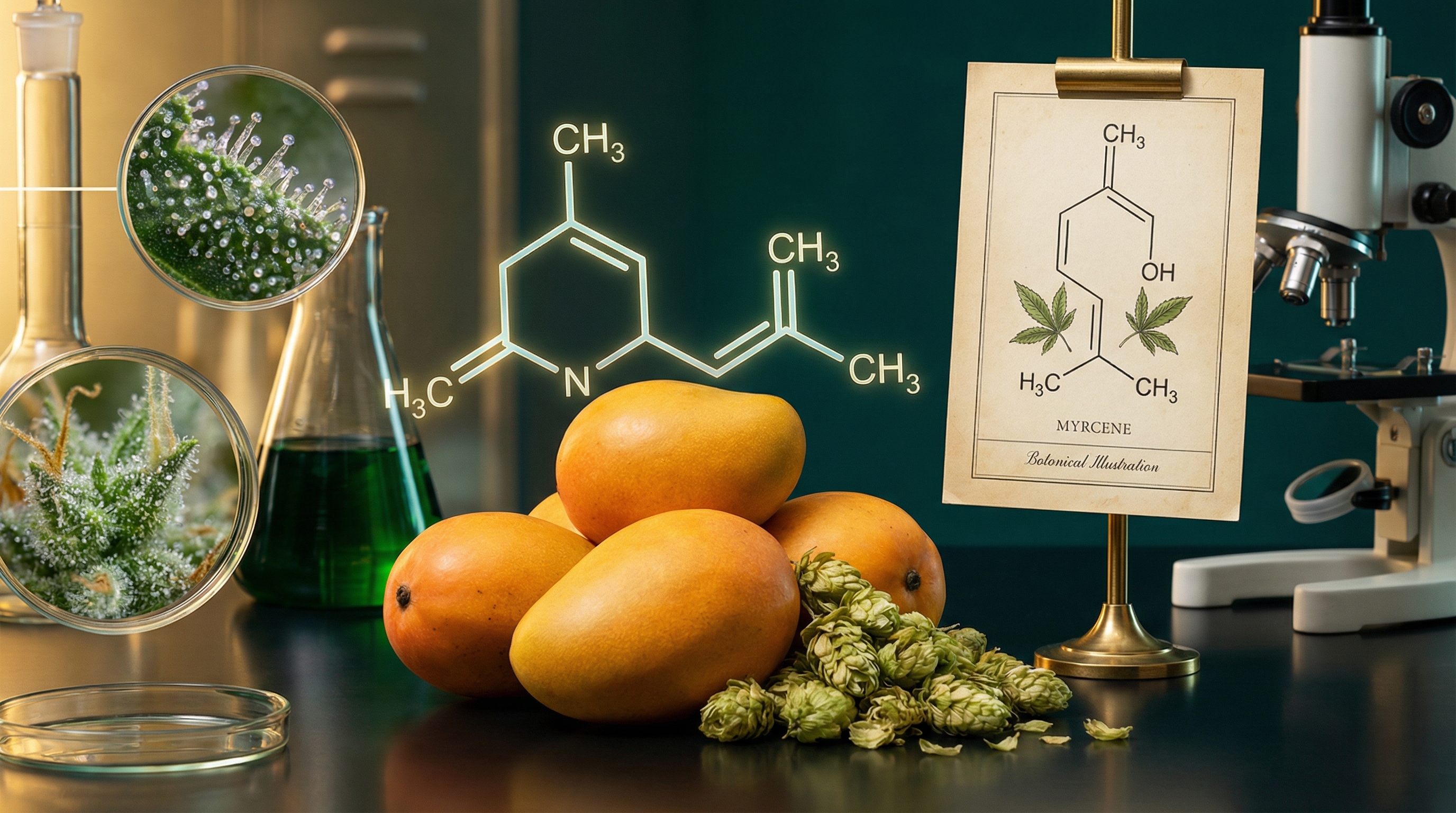
Aroma Profile
- Primary notes: Earthy, musky, herbal
- Secondary notes: Clove-like, slightly fruity
- Often described as: “Skunky,” “dank,” “hashy”
Where You’ll Find It (Beyond Cannabis)
- Mangoes (yes, the mango-before-smoking legend has some science behind it)
- Hops (the main terpene in beer - explains why IPAs can make you sleepy)
- Lemongrass
- Thyme
- Bay leaves
Effects & Research
Myrcene is associated with:
- Sedation and relaxation - It’s the terpene most linked to the “indica” experience
- Muscle relaxation - Makes it popular for physical discomfort
- Sleep support - Dominant in many nighttime strains
The Science: Myrcene doesn’t bind directly to cannabinoid receptors. Instead, research shows it increases cell membrane permeability, including the blood-brain barrier. This means it essentially helps THC reach your brain more effectively - and faster.
A 2025 study published in PAIN Journal examined myrcene-cannabinoid interplay and found that myrcene enhances the analgesic (pain-relieving) effects of THC through synergistic action on TRPV1 receptors - the same receptors that detect heat and pain from capsaicin in chili peppers.
What High Myrcene Means for Your Experience
Strains with myrcene as the dominant terpene (typically >0.5% or 5mg/g) tend to produce:
- Heavy body sensations
- Sedation, especially at higher doses
- Enhanced pain relief
- Appetite stimulation
- A “melting into the couch” feeling
Best for: Evening use, sleep support, pain management, muscle tension, unwinding after a long day.
Strains high in myrcene: Granddaddy Purple, OG Kush, Blue Dream, Grape Ape, Northern Lights.
2. Limonene: The Mood Elevator
Limonene is the second most common cannabis terpene, and it’s the reason some strains smell like you’re peeling a fresh orange. It’s associated with uplifting, mood-enhancing effects - and it has some of the strongest clinical evidence for specific therapeutic benefits.

Aroma Profile
- Primary notes: Citrus, lemon, orange
- Secondary notes: Fresh, clean, slightly sweet
- Often described as: “Zesty,” “bright,” “sunshine in a jar”
Where You’ll Find It (Beyond Cannabis)
- Citrus peels (lemon, orange, grapefruit, lime)
- Juniper berries
- Peppermint
- Rosemary
- Dill
Effects & Research
Limonene is associated with:
- Mood elevation - The “upper” among terpenes
- Stress relief - Without sedation
- Anxiety reduction - Clinically demonstrated
- Energizing effects - Popular for daytime use
The Science: Limonene has perhaps the strongest clinical evidence for specific effects of any cannabis terpene. A landmark 2024 study from Johns Hopkins and UC Boulder provided the first rigorous clinical proof of terpene-cannabinoid interaction.
In the double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with 20 healthy adults:
- 30mg THC alone: Significant anxiety, nervousness, and paranoia
- 30mg THC + 15mg limonene: Significantly reduced anxiety while maintaining THC benefits
- Limonene alone: No notable effects
This is huge. It means limonene doesn’t just “feel” like it reduces anxiety - it clinically, measurably reduces THC-induced anxiety in controlled human trials.
What High Limonene Means for Your Experience
Strains with limonene as a dominant terpene tend to produce:
- Elevated mood without sedation
- Mental clarity and focus
- Reduced anxiety (even at higher THC levels)
- Energetic, social effects
- A “sunny” disposition
Best for: Daytime use, social situations, creative work, managing anxiety, mood support.
Strains high in limonene: Super Lemon Haze, Lemon Skunk, Durban Poison, Jack Herer, Wedding Cake, Do-Si-Dos.
3. Pinene: The Mental Clarity Terpene
Pinene is the most common terpene in the natural world - it’s why forests smell like… well, forests. In cannabis, it’s associated with alertness, mental clarity, and may even help counteract some of THC’s memory-impairing effects.

Aroma Profile
- Primary notes: Pine, fresh, forest
- Secondary notes: Woodsy, slightly herbal, rosemary-like
- Often described as: “Walking through a pine forest,” “Christmas tree,” “crisp”
Where You’ll Find It (Beyond Cannabis)
- Pine needles and pine resin
- Rosemary
- Basil
- Dill
- Parsley
- Eucalyptus
Two Forms: Alpha and Beta
Pinene exists in two forms:
- Alpha-pinene (α-pinene): The “pine” form - produces that classic conifer scent
- Beta-pinene (β-pinene): More herbal, with notes of dill, parsley, and rosemary
Both forms share similar effects, though alpha-pinene is more common in cannabis and has been more extensively studied.
Effects & Research
Pinene is associated with:
- Alertness and mental clarity - The “wake up” terpene
- Memory support - May counteract THC’s short-term memory effects
- Bronchodilation - Opens airways, easier breathing
- Anti-inflammatory properties - Particularly in respiratory pathways
The Science: A 2024 study on pinene’s neuroprotective effects found that alpha-pinene protects neurons against beta-amyloid damage - the protein plaques associated with Alzheimer’s disease. While this doesn’t mean cannabis cures Alzheimer’s, it suggests pinene-rich strains may support cognitive health.
Perhaps more relevant for everyday use: pinene has been shown to inhibit acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine (a neurotransmitter crucial for memory). This mechanism may explain why pinene-dominant strains often produce clearer-headed experiences without the “foggy” feeling some people get from high-myrcene strains.
What High Pinene Means for Your Experience
Strains with significant pinene content tend to produce:
- Alert, clear-headed effects
- Less short-term memory impairment than average
- Easier breathing (especially for consumers with respiratory sensitivity)
- A sense of freshness and mental sharpness
- Less couch-lock, more functional experiences
Best for: Morning use, productivity, creative work requiring focus, outdoor activities, consumers who dislike “foggy” highs.
Strains high in pinene: Jack Herer, Snoop’s Dream, Blue Dream (moderate), Dutch Treat, Romulan.
4. Linalool: The Calming Terpene
Linalool is why lavender has been used for relaxation for thousands of years - and it’s the same reason certain cannabis strains produce such deeply calming effects. If you’ve ever felt a strain produce spa-like relaxation without heavy sedation, you’ve likely encountered a linalool-dominant profile.

Aroma Profile
- Primary notes: Floral, lavender, sweet
- Secondary notes: Slightly spicy, citrus undertones
- Often described as: “Spa-like,” “perfumey,” “romantic”
Where You’ll Find It (Beyond Cannabis)
- Lavender (the primary source)
- Coriander
- Sweet basil
- Bergamot
- Jasmine
- Rose
Effects & Research
Linalool is associated with:
- Calming effects - Reduces anxiety without heavy sedation
- Sleep support - Through relaxation rather than knockout sedation
- Anti-anxiety properties - One of the most studied terpenes for this use
- Mood stabilization - Gentle, consistent effects
The Science: Linalool has been extensively studied for anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) properties, both in cannabis and in aromatherapy research.
A 2024 study on linalool’s anxiolytic properties in mice found that linalool produces significant anxiety reduction through modulation of NMDA glutamate receptors and GABA receptors - the same systems targeted by pharmaceutical anti-anxiety medications like benzodiazepines, but through a different, gentler mechanism.
Importantly, linalool appears to produce calming effects without the tolerance buildup or dependence risk associated with pharmaceutical anxiolytics.
What High Linalool Means for Your Experience
Strains with significant linalool content tend to produce:
- Gentle, spa-like relaxation
- Reduced anxiety and stress
- Sleep support without next-day grogginess
- A sense of tranquility and calm
- Balanced experiences that don’t overwhelm
Best for: Evening wind-down, stress relief, anxiety management, meditation, gentle relaxation without incapacitation.
Strains high in linalool: Lavender (naturally), Do-Si-Dos, Zkittlez, LA Confidential, Amnesia Haze, Grandaddy Purple.
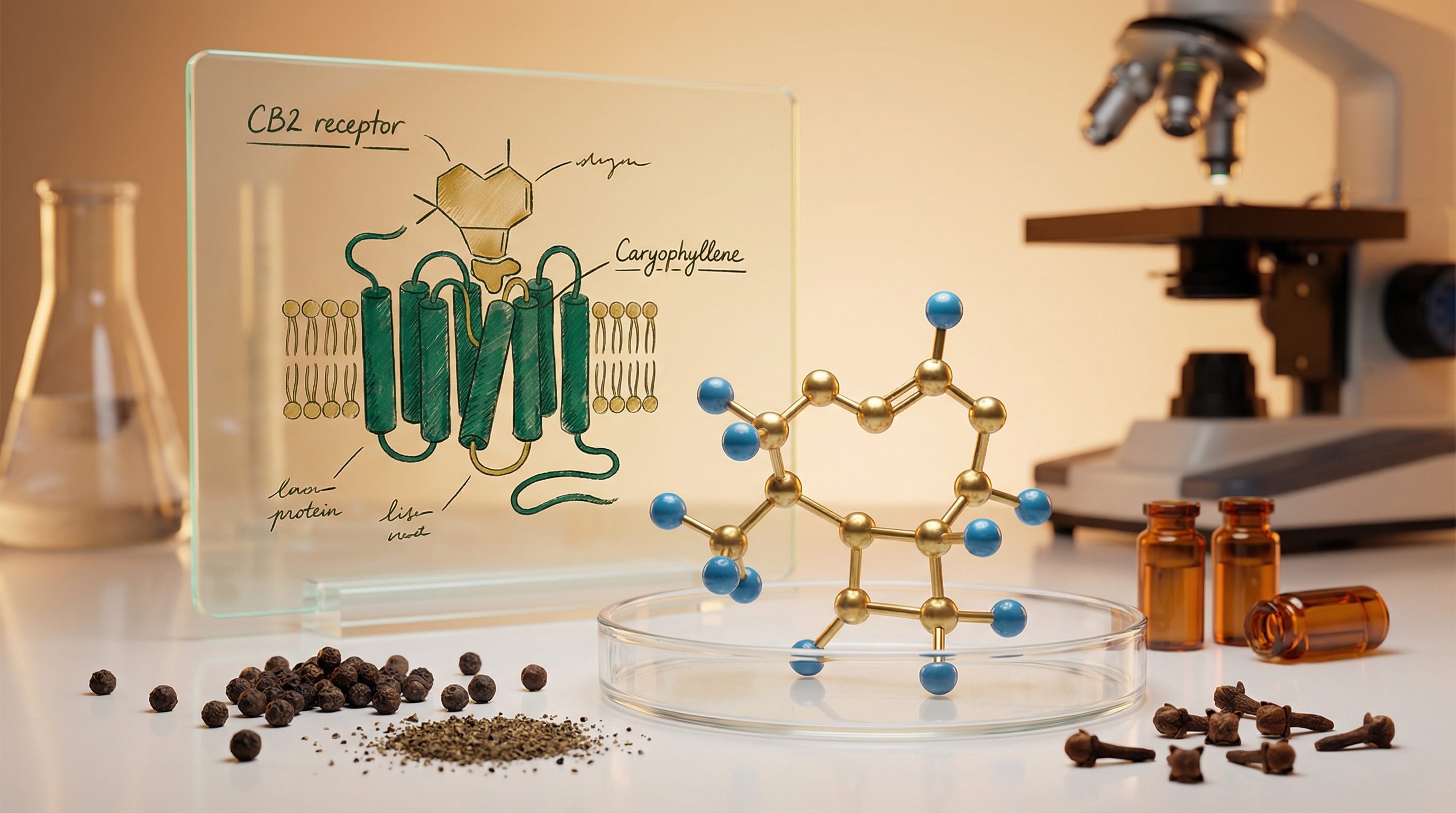
5. Caryophyllene: The Only Terpene That’s Also a Cannabinoid
Caryophyllene is unique among terpenes - it’s the only one proven to directly activate cannabinoid receptors. This makes it technically both a terpene AND a cannabinoid, bridging two worlds of cannabis chemistry.

Aroma Profile
- Primary notes: Spicy, peppery, woody
- Secondary notes: Warm, clove-like, slightly fuel-like
- Often described as: “Black pepper,” “spicy,” “warm and complex”
Where You’ll Find It (Beyond Cannabis)
- Black pepper (cracking fresh pepper releases caryophyllene)
- Cloves
- Cinnamon
- Oregano
- Basil
- Hops
The CB2 Connection
Here’s what makes caryophyllene special: it’s a selective CB2 receptor agonist with a binding affinity (Ki) of 155 nM - strong enough to produce real physiological effects.
CB2 receptors are found primarily in your:
- Immune system
- Peripheral nervous system
- Gut
- Spleen
Unlike CB1 receptors (which THC activates to produce the “high”), CB2 activation doesn’t produce psychoactive effects. Instead, it triggers anti-inflammatory cascades and pain modulation - which is why caryophyllene is associated with physical relief rather than mental effects.
Effects & Research
Caryophyllene is associated with:
- Anti-inflammatory effects - Through direct CB2 activation
- Pain relief - Especially for inflammatory pain
- Stress relief - Without sedation or intoxication
- Gastro-protective properties - May support digestive health
The Science: Research published in Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy confirms caryophyllene as a full CB2 agonist capable of producing significant anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects independent of THC.
This means when you consume cannabis high in caryophyllene, you’re getting cannabinoid receptor activation from the terpene itself - not just THC. It’s essentially a dietary cannabinoid disguised as a terpene.
What High Caryophyllene Means for Your Experience
Strains with high caryophyllene content tend to produce:
- Notable physical relief and comfort
- Anti-inflammatory benefits
- Reduced stress without cognitive impairment
- Warmth and relaxation in the body
- A “grounding” quality to the experience
Best for: Pain management, inflammation, physical recovery, stress relief, consumers seeking body effects.
Strains high in caryophyllene: GSC (Girl Scout Cookies), OG Kush, Bubba Kush, Chemdog, Original Glue (GG4), Cookies and Cream.
6. Terpinolene: The Rare Uplifter
Terpinolene is the least common of the Big 6, but strains that have it as their dominant terpene are among the most unique in the cannabis world. If you’ve ever encountered a strain with an almost indescribable, complex aroma that seems to combine floral, herbal, and citrus notes, terpinolene was likely at play.

Aroma Profile
- Primary notes: Floral, herbal, piney
- Secondary notes: Slightly citrus, fresh, almost lilac-like
- Often described as: “Complex,” “hard to pin down,” “fresh but sweet”
Where You’ll Find It (Beyond Cannabis)
- Nutmeg
- Tea tree
- Cumin
- Apples
- Conifers
- Lilac
The Rare Bird of Cannabis
Terpinolene-dominant strains are genuinely uncommon. In the 2025 German study of 140 strains, only 6 strains (4.3%) fell into the terpinolene-dominant cluster. This rarity makes them special finds for consumers who prefer their effects.
Effects & Research
Terpinolene is associated with:
- Uplifting effects - Creative, energetic, motivated
- Mental stimulation - Active rather than passive
- Antioxidant properties - Among the strongest of common terpenes
- Mild sedation at high doses - Paradoxically calming when concentrations are very high
The Science: Terpinolene shows strong antioxidant and potential anticancer activity in preclinical research. More relevant for everyday use, terpinolene-dominant strains consistently produce unique, uplifting experiences that users describe as distinctly different from limonene-dominant “energetic” strains - more cerebral and creative, less purely stimulating.
What High Terpinolene Means for Your Experience
Strains with terpinolene dominance tend to produce:
- Creative, inspired mental states
- Uplifted, motivated energy
- A unique “heady” experience
- Effects that feel distinctly different from other strains
- Sometimes paradoxical mild sedation at very high doses
Best for: Creative work, inspiration, unique experiences, consumers bored with typical strain effects.
Strains high in terpinolene: Jack Herer, Durban Poison, Ghost Train Haze, Golden Pineapple, Dutch Treat, XJ-13.
How to Use Terpene Knowledge in the Real World
Understanding terpenes is great, but you need practical application. Here’s how to actually use this knowledge when shopping for cannabis.
Reading Lab Results
Most legal dispensaries provide COAs (Certificates of Analysis) for their products. Here’s what to look for:
Total Terpene Content:
- Below 1%: Low terpene content, may lack entourage effect
- 1-2%: Average terpene content
- 2-4%: Rich terpene profile, strong entourage potential
- Above 4%: Exceptionally terpy (rare, often found in fresh cured or live products)
Dominant Terpene: The terpene with the highest percentage will most strongly influence your experience. Match it to your desired effects:
| Desired Effect | Look For Dominant | Avoid Dominant |
|---|---|---|
| Relaxation/Sleep | Myrcene | Terpinolene, Limonene |
| Energy/Focus | Limonene, Pinene, Terpinolene | Myrcene |
| Pain Relief | Caryophyllene, Myrcene | - |
| Anxiety Relief | Limonene, Linalool | High Pinene (can be stimulating) |
| Creativity | Terpinolene, Limonene | High Myrcene |
Why “Indica vs Sativa” is Outdated
Here’s the truth that the cannabis industry is slowly accepting: sativa and indica labels tell you almost nothing about how a strain will affect you.
A 2025 German study analyzed 140 strains and found no statistical correlation (p > 0.05) between indica/sativa classification and terpene profiles. None.
What does predict effects? Terpene profiles. A “sativa” with 3% myrcene will make you sleepier than an “indica” with dominant limonene. The labels are based on plant morphology (leaf shape, growth patterns), not chemistry or effects.
The practical takeaway: Stop asking “Is it sativa or indica?” and start asking “What’s the dominant terpene?”
Building Your Terpene Preferences
Keep a simple log of strains you’ve enjoyed:
- Note the strain name
- Record the dominant terpene(s) from lab results
- Rate your experience
- Look for patterns
After trying 10-15 strains with notes, you’ll likely discover you consistently prefer certain terpene profiles. This knowledge is far more useful than relying on strain names (which vary wildly between growers) or indica/sativa labels (which are scientifically meaningless).
FAQs
Do terpenes get you high?
No - with one exception. Terpenes don’t produce intoxication on their own (except for mild aromatherapy effects). However, beta-caryophyllene activates CB2 receptors, which technically makes it a cannabinoid, though CB2 activation doesn’t produce a “high.”
Terpenes’ real power is modulating how cannabinoids affect you. They’re the difference between a sleepy high and an energetic high, an anxious experience and a calm one.
Can I use essential oils to add terpenes to cannabis?
Technically yes, but it’s complicated. Adding food-grade limonene to a THC product would theoretically enhance mood-elevating effects. However:
- Dosing is tricky (too much can irritate)
- Not all essential oils are safe to inhale
- The natural ratios in cannabis are likely more effective
- It’s easier to just choose a naturally terpy strain
Do terpenes survive smoking/vaping?
Partially. Different terpenes have different boiling points:
| Terpene | Boiling Point |
|---|---|
| Myrcene | 167°C (332°F) |
| Limonene | 176°C (349°F) |
| Linalool | 198°C (388°F) |
| Caryophyllene | 160°C (320°F) |
| Pinene | 155°C (311°F) |
Vaping at lower temperatures (160-180°C / 320-356°F) preserves more terpenes than smoking, which occurs at higher, less controlled temperatures.
How do I find high-terpene strains?
Look for:
- Fresh flower - Terpenes degrade over time
- Proper storage - UV light and heat destroy terpenes
- Lab-tested products - With terpene percentages listed
- Live resin/rosin - Made from fresh-frozen plants, preserving terpenes
- Total terpene content above 2%
Do all batches of the same strain have the same terpenes?
Not exactly. Terpene profiles can vary between:
- Different growers
- Different harvests
- Different phenotypes of the same strain
- Different curing and storage conditions
Strain names are a starting point, but always check lab results when available.
Key Takeaways
Terpenes are aromatic compounds that shape how cannabis affects you - they’re produced in trichomes alongside cannabinoids and contribute to effects through multiple mechanisms.
The Big 6 terpenes cover most cannabis experiences:
- Myrcene: Sedating, relaxing, “couch-lock”
- Limonene: Mood-elevating, anxiety-reducing, energizing
- Pinene: Mental clarity, alertness, memory support
- Linalool: Calming, anti-anxiety, spa-like relaxation
- Caryophyllene: Pain relief, anti-inflammatory, the only terpene that’s also a cannabinoid
- Terpinolene: Creative, uplifting, rare and unique
Sativa/indica labels are scientifically meaningless for predicting effects - terpene profiles are what actually matter.
The entourage effect is real - the 2024 Johns Hopkins study proved that limonene specifically reduces THC-induced anxiety in controlled human trials.
Look at lab results when shopping - aim for 1-4% total terpenes with a dominant terpene that matches your desired experience.
Continue Your Cannabis Education
Want to go deeper into cannabis science? Check out these related guides:
- The Entourage Effect Explained - How cannabinoids and terpenes work together for enhanced effects
- How to Read Cannabis Lab Results - Make sense of COAs and test results
- The Science Behind High Families - How we classify strains by chemistry, not marketing
Explore our High Families to find strains matched to your preferred terpene profiles, or browse individual terpene pages for strain recommendations.
Sources:
Herwig N, et al. (2025). “Classification of Cannabis Strains Based on their Chemical Fingerprint.” Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research 10(3):409-419. DOI: 10.1089/can.2024.0127
Spindle TR, et al. (2024). “Vaporized D-limonene selectively mitigates the acute anxiogenic effects of Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol.” Drug and Alcohol Dependence 257:111267. PubMed
Francomano F, et al. (2021). “Beta-Caryophyllene: A Sesquiterpene with Countless Biological Properties.” Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 140:111767.
Guimaraes AG, et al. (2024). “Linalool attenuates anxious behavior through modulation of GABA and glutamate neurotransmission.” MDPI Molecules 29(4):892.
Shin M, et al. (2024). “Alpha-pinene exhibits neuroprotective effects against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity.” ScienceDirect Neuropharmacology 198:109462.
Kogan NM, et al. (2025). “Cannabis terpenes act as agonists on endogenous cannabinoid receptors.” Israeli Medical Association Journal 27(2):89-94.